A quieter revolution is taking place in the midst of all that modernity in a contemporary hospital, where beeping monitors and running footsteps resound through different corridors. It's not a new surgical technique or another pharmaceutical breakthrough. It's much, much smaller but just as transformative - wearable devices. System Testing Services validate the devices' performance and safety in real-world healthcare environments by involving seamless integration into medical systems.
Imagine a busy conference room full of doctors, nurses, IT specialists, and regulatory officials trying to figure out the net negative side of making wearables a mainstay in everyday medical practice. Who can even round it up, from remote patient monitoring to predicting illnesses before they have symptoms?
"But amid all the excitement, one burning question remains unanswered. What is the accuracy of these devices? Will they be able to supplement traditional medical diagnostic tests? What assures us our data will not become public?"
It is more than a tale - it is the story of human ingenuity and cooperation in making tomorrow healthier. And indeed, the role of wearables testing is to ultimately transform the primary hospitals and laboratories across the globe in church and health initiatives.
This is how technology is transforming the healthcare space - Very much. Let's start.
Table of Contents
- What is Wearable Technology in Healthcare?
- What is the Importance of Wearable Technology in Healthcare?
- Advantages of Wearable Testing Technologies in Shaping Healthcare
- Navigating Challenges of Wearable Testing in Healthcare
- Future of Wearable Testing in Healthcare
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Wearable Technology in Healthcare?
Wearable technology in the healthcare domain marks a paradigm shift wherein the cute little gizmos become everyday accoutrements one now has to wear, collating and converting raw inputs into health outputs. People are put under constant surveillance in the privacy of their homes. Imagine smartwatches monitoring heartbeats, wearable patches gauging glucose, administering drugs, and then using empty talk about life changes; these wearable gizmos change life. They've opened up highly excellent avenues in healthcare toward consumers and practitioners accessing physiological parameters earlier available in bits of data sporadically during clinic visits.
In addition, other dimensions of personal usage include chronic disease management and prevention. Such devices can help in early detection of abnormal and corrective action before needing additional measures that can save costs.
Also, their capacity to support ongoing observation and tailored feedback promotes a more patient-centered approach to healthcare delivery, improving users' quality of life in general. The potential of this technology in healthcare seems limitless, offering a future where proactive, individualized health management is not just a possibility but a standard as the industry continues to innovate, merging artificial intelligence and advanced sensors.
Have a look at some facts and figures!
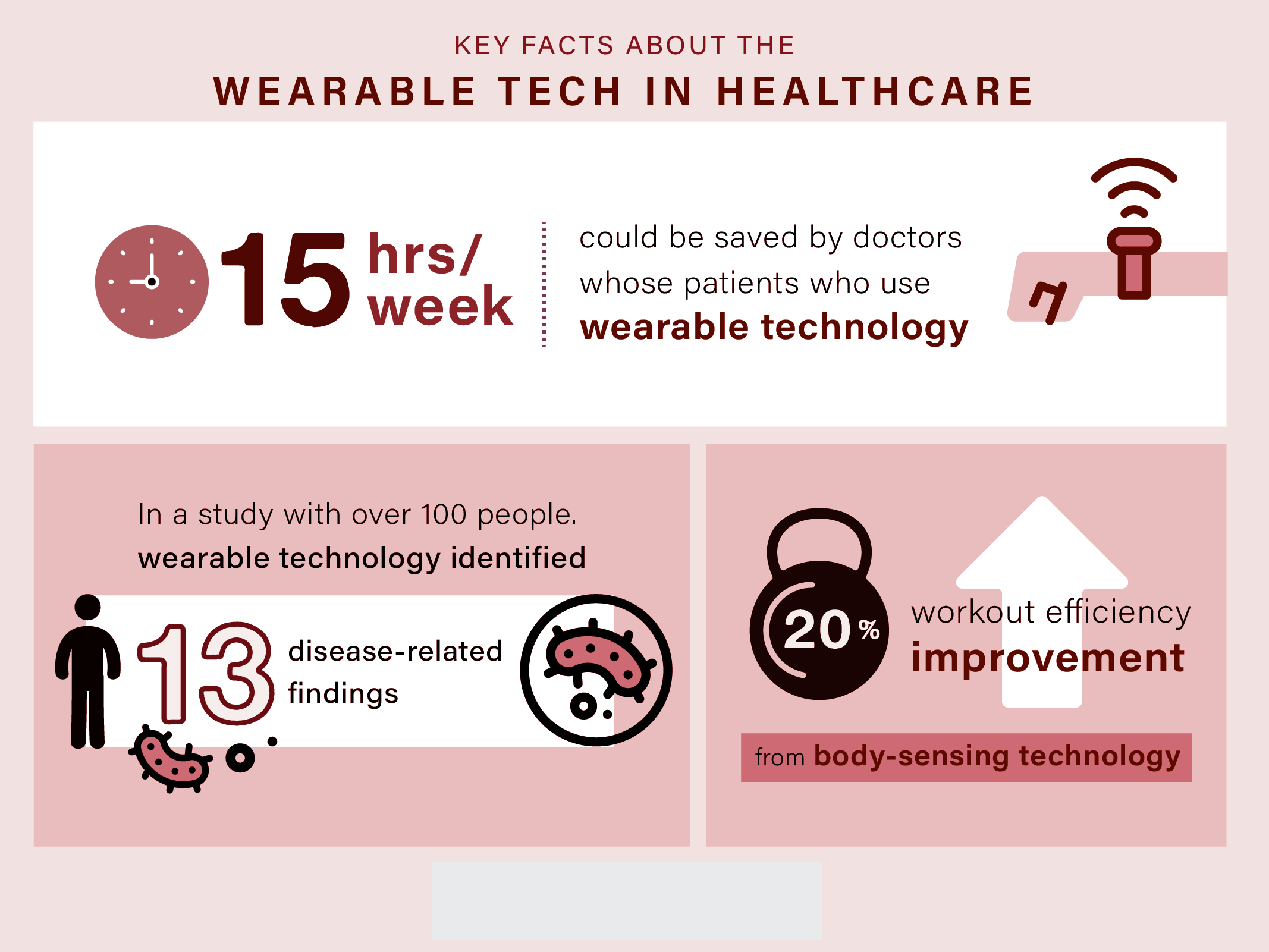
What is the Importance of Wearable Technology in Healthcare?
- Continuous Monitoring and Early Detection: Wearable technologies allow for continuous monitoring of vital signs such as blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and heart rate. Because of this continuous stream of information, even in the absence of symptoms, an attribution of health problems can be detected early. So, for example, abrupt variations in blood sugar levels and unusual heartbeats can be found, triggering early and preventive action by medical treatment when necessary to avoid consequences.
- Enhanced Patient Engagement and Empowerment: Wearable technologies actually help keep patients actively involved in their health management. It provides insights that are individualized and instantaneous feedback from the gathered data to promote better living. The more the patient feels engaged in the health treatment, the more adherence to treatment plans improves the overall outcome.
- Support for Remote and Telehealth Services: It facilitates remote monitoring and telehealth appointments within the growing digital health environment. Healthcare providers can access patient data from remote areas, assess data longitudinally, and make well-informed decisions without requiring regular in-person visits. Increased access to healthcare is brought about while concomitantly alleviating the burden on conventional health systems. It benefits in the management of chronic diseases, elderly care, and rehabilitation post-surgery.
Advantages of Wearable Testing Technologies in Shaping Healthcare
1. Early Disease Detection
Anomalous heartbeats, faulty blood glucose levels, or irregularities in sleep may all present as early symptoms of a rising health situation. Wearable testing technologies can be geared toward continuous monitoring of vital signs and biomarkers, which will then put the individual on a fast track to early diagnosis. Taking immediate action may avert major health complications.
2. Personalized Medicine
The wearable testing tech provides facility-oriented care by collecting real-time information on the health indicators of an individual. This information-based method allows health professionals to make decisions concerning the individual's treatment by personalizing plans and actions according to the unique needs and responses of each patient.
3. Improved Patient Engagement and Adherence
Wearable technology advancements encourage active patient participation in their own healthcare management. Continuous monitoring and feedback create a more engaging environment for the adoption of good habits and compliance with recommended therapies, thereby improving the overall health outcome.
4. Enhanced Remote Monitoring and Telehealth
Testing technologies such as these allow medical personnel to monitor a patient's health from afar or in the comfort of their home, thus reducing the need for constant visits to the clinic. This proves especially helpful in cases of geriatric care, post-operative rehabilitation, and management of chronic illnesses. The technology also fast-tracks timely interventions and reduces healthcare costs.
5. Real-Time Health Monitoring and Alerts
Fitness and medical studies, and large-scale health research programs, can benefit from aggregated data from wearable devices. The creation of new healthcare technologies, public med-initiatives, and efforts to prevent disease can all benefit from these insights about trends and patterns across a range of populations.
Navigating Challenges of Wearable Testing in Healthcare
1. Integration with Existing Healthcare Systems
Integration of wearables with healthcare infrastructure is another problem that it confronts with their current programs and newly updated ones. To provide patients and caregivers with the necessary support, it must relate to a high-quality healthcare infrastructure. In an emergency, medical technology cannot fully assist a patient if the hospital is not there to support it.
Software developers take on the task of integrating a wearable device with the entire medical infrastructure. Even though it can be unthinkably complex, development teams can effortlessly integrate something so huge with something small.
2. Accuracy and Reliability of Wearable Devices
Wearable technology can occasionally perform less accurately and reliably than anticipated. Its healthcare assistant technologies, for example, should have great accuracy because data is vital. Certain procedures might not finish as planned if precision and dependability are lacking. The patient may have difficulties and serious obstacles that result in device failure and health problems.
3. Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Concerns about data security and privacy may also surface. These worries may result in noncompliance and other gadget malfunctions. Data and personal information about individuals may be compromised when data privacy and security are breached.
Healthcare electronic devices may give rise to data security and privacy issues. Since these devices are online, there may be persistent worries about data security and privacy due to the data transmission. Implementing proper security testing and reinforcements, data security and privacy measures can be implemented in a better way.
4. Regulatory and Compliance Issues
The wearable device development company also has a lot of regulatory and compliance challenges to deal with. This electronic gadget must adhere to industry standards and regulations because it will be employed in the healthcare field. To prevent legal complications for the device, it is imperative that the regulatory and compliance issues are promptly handled. For the device to be fully functional and commercially viable, it must satisfy industry requirements.
Future of Wearable Testing in Healthcare
1. Integration with AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning will be used to power this technology in the upcoming generation. These innovations will provide predictive analytics and individualized health advice by analyzing the massive amounts of data produced by wearables. This will make proactive health management possible, in which medical related problems are found early on and resolved before they worsen.
2. Greater Interoperability and Data Sharing
More extensive and well-coordinated care will be possible with enhanced electronic device and electronic health record (EHR) compatibility. Data exchange between patients and healthcare professionals will be smooth, enabling more informed clinical judgments and individualized treatment strategies.
3. Expansion in Telehealth and Remote Care
The development of wearable testing technology will be essential to the growth of telehealth offerings. The experience of remote patient monitoring will increase, enabling prompt interventions and real-time modifications to treatment plans. This is especially helpful for treating patients in underserved or remote locations and controlling chronic illnesses.
4. Enhanced Sensor Technology
More advanced and varied sensors that can more precisely monitor a larger variety of physiological features will be incorporated into wearable technology in the future. With the ability to monitor anything from hydration levels and blood sugar levels to mental health indicators, these sensors might provide a comprehensive picture of a person's health.
5. Focus on Preventive Healthcare
By providing around-the-clock, real time monitoring of medical markers, wearable technologies will shift the health paradigm from reactive to preventive. People and healthcare professionals can then take the initiative in the fight against disease and health maintenance by identifying risk factors and minor signals of an issue.
Conclusion
The revolutionizing smart health in relation to the medical field is that it has finally opened a new avenue of opportunity through wearable device testing. This new technology provides real-time updates, earlier recognition, and personalized care, closing the gap between patients and their healthcare professionals and rendering the impossible possible. This tech-science will allow a general population to take measure of their health through continuous assessment of vital and other medical parameters. It also gives professionals the information they need to make educated decisions, provided these devices are thoroughly validated, often with the help of a Software Testing Company to ensure accuracy and reliability.
The significance of wearables in the time ahead will manifest with the incorporation of AI and more advanced sensor technologies, as well as improved transmission of information. These advances have the potential to bring very large population benefits for the improvement of health outcomes and reductions in costs by shifting treatment from reactiveness to prevention. Such an advancement in technology will continue to pave new paths in the burgeoning arena of medical innovation through the dedication to ever-increasing accuracy, user experience, and remote care capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do wearable devices contribute to healthcare transformation?
It transforms healthcare by continuously monitoring and gathering vital signs and other variables, and making real-time data available to patients and healthcare providers. This allows early diagnosis of medical conditions, individualizing treatments, and proactive healthcare management. Wearables also enable telehealth and remote monitoring, increasing patient access to care and minimizing frequent in-person visits.
2. What types of health metrics can wearable devices monitor?
Wearable technology can monitor numerous health parameters like heart rate, blood pressure, glucose levels, oxygen saturation, sleep patterns, physical activity, and even indicators of mental health. It is also beginning to monitor physiological parameters such as respiration rates and hydration levels.
3. How accurate are wearable devices in monitoring health metrics?
Wearable device accuracy has greatly improved over the years due to advances in sensor technology and data analysis algorithms. While not all wearable devices are meant to serve medical purposes, many are indeed reliable enough for use in everyday health monitoring and can provide valuable insights when used together with professional medical guidance.
4. What role does AI play in wearable device testing?
Artificial intelligence (AI) in wearable device testing plays an immense role through mining the vast amount of data these devices produce. The AI provides personalized health recommendations, predicts possible health conditions, and helps in recognizing patterns. AI further helps provide improved accuracy and efficiency for the benefit of the patient and the healthcare practitioner.
5. Can wearable devices replace traditional medical diagnostics?
With the intention of supplementing conventional medical diagnostics, and not to supplant it, these techniques provide continuous real-time monitoring, which can improve the management of chronic diseases by offering early warning signs. In all such cases, however, expert clinical evaluation and testing are essential for conclusive diagnosis and treatment.