Regression testing ensures that the software's functionality is reliable and consistent from the time of its conception to the time of any future upgrades. When regressions are tested, both the development team and stakeholders are able to assure themselves that their application remains consistent with the originally intended functional requirements, even with the ongoing changes and updates.
Here, we will provide an overview of regression testing, reviewing its importance, methods, best practices, and various tools used to support the effectiveness of this critical quality control process.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Regression Testing?
- Top Regression Testing Tools
- Regression Testing Techniques
- Advantages of Regression Testing
- Disadvantages of Regression Testing
- Conclusion
Introduction
Regression testing is an important constituent of the development cycle that requires re-execution of already tested code compared to its previously executed state to demonstrate that recent changes have not adversely affected current features. The purpose of such tests is to detect previously unknown faults that might have been introduced inadvertently during changes or upgrades. The software is therefore retested in some areas again to ensure stability and functionality across different cycles through regression testing. Regression Testing Services ensure the software's quality and reliability for the user experience, thereby minimizing the possibility of errors.
Regression testing checks that any changes made to current codes do not bring in accidental new bugs or upset existing processes. This is where regression testing comes into play. An important part of the quality assurance process, it checks whether recent modifications in code have damaged current modifications. In addition, it involves re-running tests over the impacted parts of the software to check that everything still behaves as expected after modifications or enhancements.
Picture a situation in which a group of developers is collaborating on a web application. They introduce a new element, like a user authentication system, and conduct extensive testing to ensure it operates perfectly. Although a couple of weeks later, they incorporate an additional feature or resolve an issue in a different section of the software.
Now the question is: Have these changes unintentionally affected the performance of the existing user authentication system? This is when regression testing proves to be extremely helpful. The QA team can promptly detect any unintended side effects from recent changes by running the necessary tests for the authentication feature.
What is Regression Testing?
- Regression testing makes sure that modifications to software code do not cause any existing functionalities to fail. It requires running tests again to make sure that recent changes didn't introduce any unforeseen issues or "regressions" in how the application functions. This aids in keeping the software stable and avoiding the addition of new bugs.
- A major objective of regression testing is to identify and suppress new defects/'regressions' from being introduced into the software, which may occur if an alteration on a specific section of code unintentionally affects other parts of the program, and results in a previously working feature now working incorrectly.
- By re-running various test case scenarios applicable to important features, edge cases, and user interactions, regression testing helps developers and QA detect any deviations from expected performances caused by recent changes.
It ensures that the software stays stable, dependable, and free of bugs during its entire lifespan.
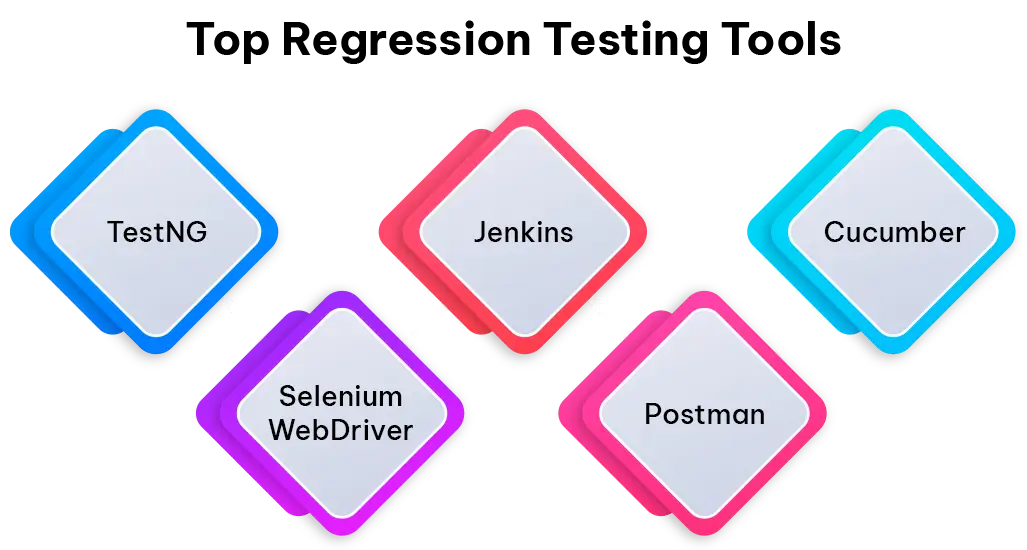
- TestNG:TestNG is an alternative testing framework for Java applications, providing a greater range of features compared to JUnit. Parameterized tests, test grouping, and parallel execution are all supported, making it ideal for conducting regression testing in extensive projects.
- Selenium WebDriver: Selenium is a testing framework for web applications that is open-source and created for that purpose. Selenium WebDriver is a commonly chosen tool for conducting regression testing on web applications, within its array of components. This technology enables the automation of browser actions on various browsers and platforms, offering flexibility to guarantee the stability and dependability of web-based software products.
- Jenkins: Jenkins is one of the most widely used automation servers; its major strength lies in its being open-source, which facilitates the smooth creation of CI/CD pipelines for use in continuous integration and continuous delivery workflows. It automatically runs regression test suites when there are codebase changes.
- Postman: Postman is a facility on which highly sought after of API testing. Users can develop automated tests for REST API and also can execute them through it. The determination capability is an admirable feature that makes Postman hold an upper hand while performing regression tests on various API endpoints.
- Cucumber: Cucumber provides the framework that conforms to Behavior-Driven Development (BDD). It serves as a means to creating test cases in plain text through the Gherkins. It hence fosters cooperation among people with dissimilar skill sets and is also much applicable in regression testing within agile environments.
Regression Testing Techniques
- Repeat All Tests: This method includes running all current test cases again, testing all features of the software. Even though it is comprehensive, this approach may demand significant amounts of time and resources.
- Arragned Test Cases: Regression Testing with priority focuses on arranging test cases according to their importance and influence on the functionality of the software. Test cases with high priority, such as crucial functions or critical scenarios, are run before test cases with lower priority.
- Risk-Based Regression Testing: This approach assesses the risks associated with recent software changes and subsequently organizes regression tests accordingly. The probability of a regression and its possible consequences on software functionality or its users are then considered in the selection of test cases.
- Ad-hoc Regression Testing: Testing that is done is the name used in this instance. The tester investigates the areas of the software with a major focus on the special areas that could be impacted by the recent change or enhancement. Ad-hoc testing will help find unexpected problems, acting as an additional layer/protection to the formal regression testing methods.
- Smoke Testing: A rapid and superficial form of regression testing that checks if the fundamental features of the software are functioning properly post-updates. It assists in guaranteeing that the software is stable for additional comprehensive regression testing.
- Testing through Exploration: This form of testing involves simultaneously learning, creating tests, and conducting tests. Testers evaluate the software's abilities, focusing on areas that could be affected by recent changes. Exploratory testing allows for the discovery of regression problems that may go unnoticed if only using pre-planned test cases.
- Continuous Regression Testing: Continuous Regression Testing is vital in any software development with a smooth flow into the CI/CD pipeline. This approach ensures that automated tests are perpetually executed, in which regression tests run as a non-stop automated process, intervening on any code change. This feedback loop allows developers to obtain timely information on how their changes impact the system.
Advantages of Regression Testing
- Identifying regressions: Important benefits of a regression test include the detection of regressions, unintended problems or failures when the program undergoes a recent change in its codebase. Regression testing checks the changes in previously defined expected performance due to the change, i.e., by executing existing test cases.
- Maintain Software Stability: Regression testing is a critical success factor in ensuring new changes do not produce adverse effects on existing features and maintain software stability. It ensures confidence in developers, testers, and stakeholders that the software will behave as expected after additive or corrective changes.
- Proactive: Even though regression testing takes time, it ultimately saves time and resources by preventing problems early in the development process. The strategy is to stop possible issues from escalating, and in turn, make the entire development process efficient. It helps in enhancing the testing efficiency by automating the repetitive test cases and concentrating on testing for critical areas of the software, thus making the testing process efficient.
- Maintaining Customer Contentment: Ensuring a reliable and steady software application directly increases customer satisfaction levels. Regression testing is seen as an important player in ensuring software applications provide positive user experiences by reducing the chances of unexpected errors, crashes, or downtime due to regressions.
- Continuous integration: It is realized, however, that regression tests are very vital in CI/CD pipelines to assure support for Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment. Indeed, CI/CD involves rather frequent modifications in production environments. The continuous use of regression testing in the CI/CD pipeline and automated execution enables firms to be confident of completing the whole test on every code modification before user deployment. With that, the importance that makes it interesting about fast reliable software releases.
Disadvantages of Regression Testing
- Takes Up Time: Regression testing takes a significant amount of time, especially when it comes to complex software applications. Extensive regression testing can elongate the software release cycle considerably, particularly when applied after each code change.
- Demanding of Resources: Developing, executing, and monitoring test cases requires different resources such as hardware, testing environments, and skilled personnel. Assigning these resources may come with high costs, especially for companies with restricted budgets or strict timelines.
- Regression testing: Regression testing may face difficulties like false positives or false negatives that can interrupt the testing procedure. False negatives happen when tests don't catch real regressions, whereas false positives occur when tests wrongly recognize regressions that are not there.
- Limited Coverage: It can be difficult to develop thorough regression test suites covering every scenario and edge case due to restricted time and budget. Insufficient test coverage raises the chances of regression problems being undetected until they directly affect end-users.
- Relying on Automated Testing: Even though automated testing can ensure better effectiveness and reliability of regression testing, it relies on automation frameworks, scripts, and tools. Difficulties in any of these may arise. Problems in the automated setting could interrupt testing, leading to further delays in software release.
Conclusion
Regression testing is an important quality assurance technique to ensure software stability and reliability throughout its entire software lifecycle. The constant retesting of code that has been altered prevents unintentional side effects while keeping functionality consistent with the old software version that continues to be updated. A Software Testing Company often plays a critical role in executing thorough regression testing to maintain performance and minimize post-deployment issues. The focus of the blog will be its importance, methodologies, best practices, tools, and significance in delivering a good user experience, reducing bugs, and enabling quicker development with many benefits: early defect detection and higher customer satisfaction. Nevertheless, regressions are worth doing because they tend to take time and resources, give false positives, and are limited in scope. Despite these drawbacks, its integration into CI/CD pipelines and automation frameworks remains pivotal for achieving robust and dependable software releases.
If you're still reading this post, we assume that you're planning to ensure the stability and quality of your software, aren't you? Then, experience top-notch regression testing services from PixelQA and elevate your testing process!
About Author
Vedant Parmar is a veteran QA executive who believes in continuous learning, training, and acquiring new skills. He wants to pursue a career in Mobile Test Automation and Penetration Testing, and strives to be a QA manager in his professional journey.