Table of Contents
- What is ETL testing and why do we perform ETL Testing?
- What is Big Data in ETL?
- What is a Data Warehouse?
- What is Business Intelligence (BI) software?
- Software Used for ETL Testing
- How is Transformation logic and Mapping created by BA?
- What Are the Different Types of ETL Testing?
- How to Perform ETL Testing?
- Pros and Cons of ETL Testing
- Why Is ETL Testing Still Necessary?
- Conclusion
What is ETL testing and why do we perform ETL Testing?
ETL refers to Extract, Transform, and Load. Load Testing Services in ETL is a procedure to ensure that data gets loaded from source to the target after accurate business transformation has been done.
It involves verifying data at various middle stages being used between source and destination.
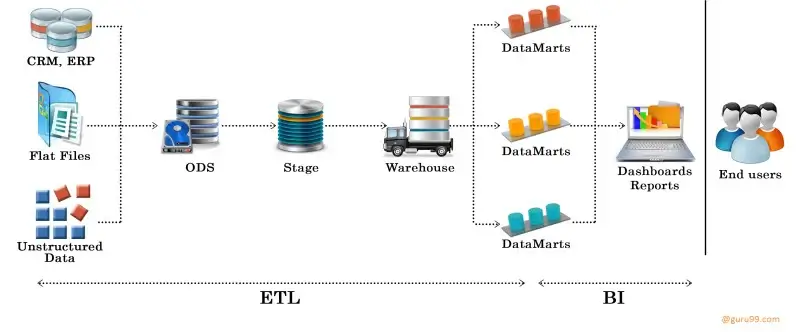
Here's a simple breakdown of the process:
Extract: Data is extracted from multiple source systems (i.e. Multiple companies sending unprocessed data to a one target system)
Transform: After extraction, data undergoes a meticulous transformation process where we clean, standardize, and restructure it to fit the warehouse schema. This stage often reveals hidden data quality issues - in one retail project, we identified and resolved 12% irregular product codes during transformation. The final step carefully loads the refined data into its new home, ensuring structural integrity.
Load: We rigorously validate each transformation against business rules, confirming data arrives complete and uncorrupted. This quality gate is indispensable - our financial clients typically see a 40% reduction in reporting errors after proper ETL testing implementation. The process safeguards data reliability across the entire analytics pipeline.
Modern data teams continuously refresh warehouses and marts, pulling from diverse sources including files, APIs, and XML feeds. Our healthcare clients, for example, automate daily loads of patient data from 14 different EHR systems into their enterprise data lake while maintaining strict HIPAA compliance throughout the pipeline.
What is Big Data in ETL?
Big Data in ETL testing means the process of validating the data extraction, data transformation and data loading of large volumes from numerous different sources into a data warehouse.
Here are some of the important aspects of Big Data in ETL testing:
Data Integrity: This checks the integrity of existing and new data with the addition of new data.
Incremental Testing: This ensures that the inserts and updates are being processed as intended in the process of incremental ETL.
Data Accuracy: There are different strategies to ensure data accuracy in large-scale data pipelines for various environments.
Handling Complex Transformations: It is difficult to test ETL when there is a lot of data that has to undergo complex transformations.
The objective of ETL testing, including Big Data, is to be able to attest that the data is sufficient for a business to make decisions based on.
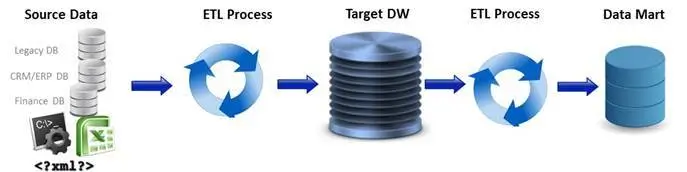
What is a Data Warehouse?
A data warehouse is the key repository for business data, aggregating data pulled from various systems of operations. With the help of the ETL process, raw data becomes cleaned, normalized, and formatted in a single form. In our work with e-commerce clients, we've seen how proper warehousing transforms disjointed data into actionable insights - one merchant improved campaign ROI tracking by 25% after implementation.
Quality assurance in data warehousing goes beyond simple validation. We methodically examine each transformation stage, verifying data integrity as information moves from source to destination. This rigorous testing ensures decision-makers can trust their analytics - financial institutions we work with typically require 99.98% accuracy before approving warehouse deployments.
Consider a retail chain where departments maintain separate customer records in different formats. Without integration, tracing a customer's journey across purchases and promotions becomes nearly impossible. We helped a national retailer solve this by creating a unified customer view, reducing customer service research time from hours to minutes while enabling personalized marketing at scale.
ETL can transform dissimilar data sets into a unified structure. Later, BI tools can be used to derive meaningful insights and reports from this data.
Data Mart
A data mart is a subset of a data warehouse that has the same characteristics but is usually smaller and is focused on the data for one division or one workgroup within an enterprise.
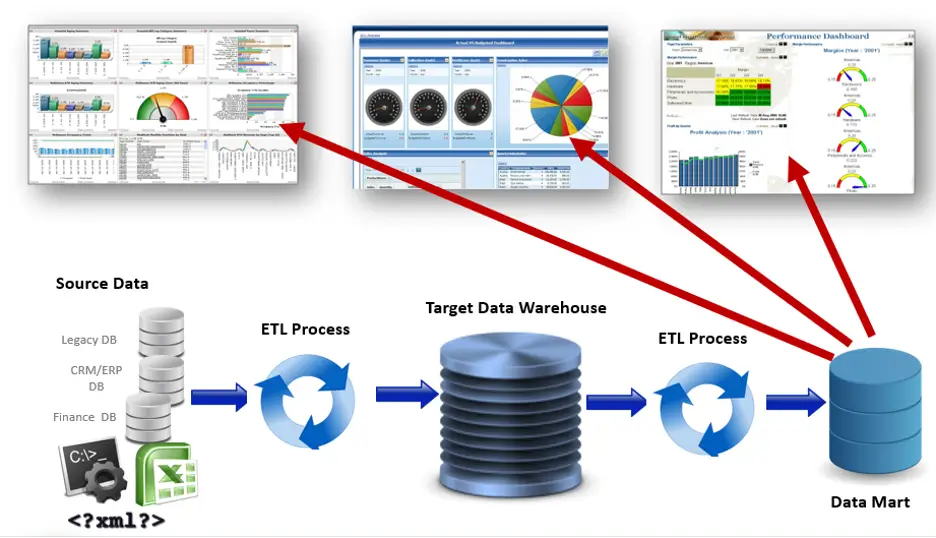
What is Business Intelligence (BI) software?
Business Intelligence (BI) software is an application that collects and processes large amounts of unstructured data from internal and external systems and prepares it for analysis. The software is generally used for querying and reporting complex business data.
Some of the examples of the BI Software are Microsoft Power BI and Tableau.
The role of BI software is to guide businesses to take correct decisions, increase revenue, improve operational efficiency and to gain an advantage over its competitors. It performs tasks for businesses, some of them are data mining, forecasting, and reporting, and visualizing data through charts and graphs by allowing users to identify current and future trends and patterns.
Modern BI tools do more than just analyze data - they empower teams to create dynamic, interactive reports that bring insights to life for stakeholders. What makes these solutions truly valuable is how they translate raw data into actionable business improvements. For example, a retail client of ours reduced inventory costs by 18% after implementing BI-driven reporting that identified seasonal purchasing patterns they'd previously missed.
Software Used for ETL Testing
Manual ETL Testing - Any SQL Database workbench to perform queries
Using ETL Tools - Informatica, DataGaps QuerySurge , ICEDQ, etc.
How is Transformation logic and Mapping created by BA?
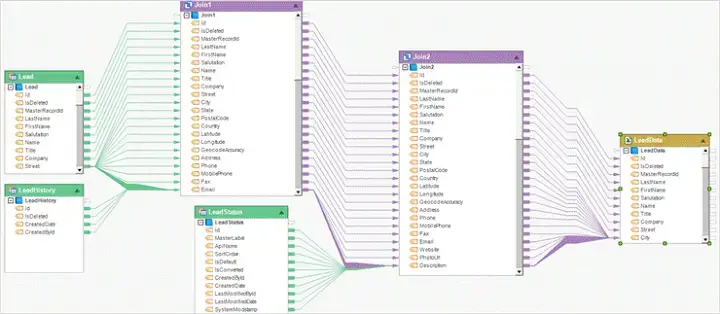
What is a Data Mapping document?
Data mapping involves matching fields from multiple datasets into a consistent schema. Mapping explains that from which table and columnthe data come from, and to which table and column does it goes after the business rules are applied.
In the ETL process, businesses collect data from different sources (like databases, APIs, or files) and transform them in between before loading it into a target system (e.g., a data warehouse).
Understanding Data Transformation:
Data transformation in the context of ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) is a critical step where raw data is refined, enriched, and shaped into a more useful format for analysis. Business Analysts (BAs) play a crucial role in defining and implementing transformation logic. Let’s explore how this process works:
- Data transformation involves modifying data to make it more meaningful or suitable for specific purposes.
- BAs collaborate with data engineers and data scientists to design and implement these transformations.
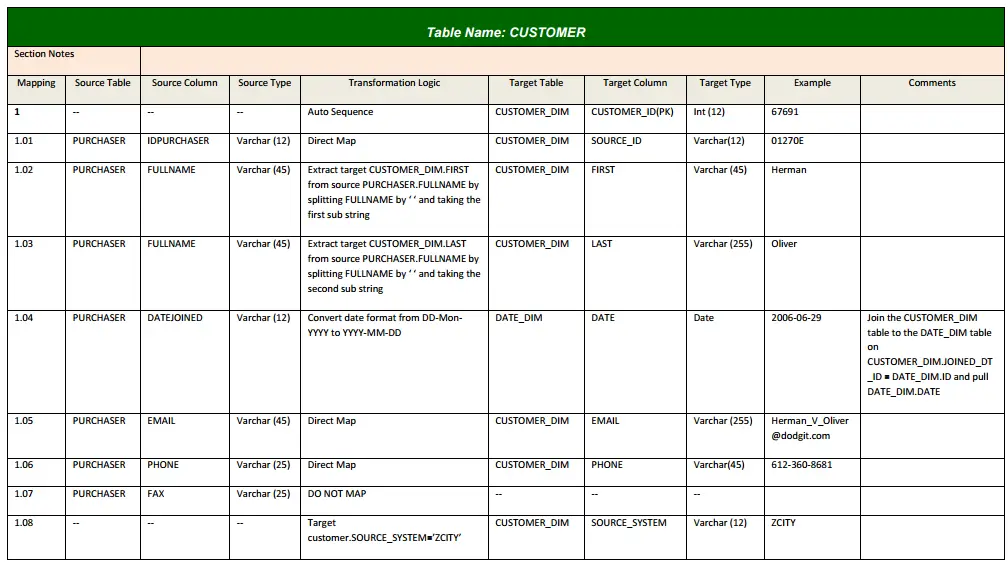
Common Business Rules/Transformation Logic Implemented by BAs:
- Cleaning and Validation: BAs ensure data quality by removing duplicates, handling missing values, and validating data against predefined rules.
- Standardization: Transforming data into a consistent format (e.g., converting date formats, normalizing text).
- Aggregation and Summarization: BAs define rules for aggregating data (e.g., calculating totals, averages, or counts).
- Deriving New Metrics: Creating custom metrics based on business requirements (e.g., customer lifetime value, churn rate).
- Data Enrichment: Combining data from different sources to enhance its context (e.g., adding geolocation information).
- Joining and Merging: Combining related data from multiple tables or datasets.
- Conditional Logic: Implementing rules based on specific conditions (e.g., categorizing customers based on purchase behavior).
Tools and Techniques to create Business Rules/Transformation logics:
- SQL Queries and Stored Procedures:BAs can define transformation logic directly in SQL queries or stored procedures within the source or target database.
- Scripting Languages (Python, R, Perl):BAs write custom code to perform complex transformations using scripting languages.
- ETL Tools (e.g., Talend, Informatica): BAs configure transformations using visual interfaces provided by ETL tools.
What Are the Different Types of ETL Testing?
Below are the types of ETL testing include:
- New Data Warehouse Testing: Verifying the data warehouse built from the core using customer's requirements and different data sources.
- Production Validation Testing/Post-Implementation Verification (PIV): Ensuring the data does not compromise production systems when data is moved to production systems. This testing is also referred to as Post Implementation Validation testing.
- Source to Target Testing (Validation): Validating the transformed data values match the expected data values.
- Application Upgrade: Checking the extracted data from an older application is precisely the same as the data in a new application.
- Metadata Testing: Includes the measurement of types of data, length of data, and check index/constraint.
Remember, ETL testing is different from database testing in terms of its scope and the steps followed during this testing. It is applied to data warehouse systems and used to obtain relevant information for analytics and business intelligence.
How to Perform ETL Testing?
Pre-requisites:
- Users will require the source database system and target database system.
- Pipelines or workflows to run the Transformation logics/Business Logics and Transfer the data to the target system.
- Mapping document provided by BAs.
- Created Test cases from the Mapping document.
Here are the checks to perform ETL testing:
- Compare the count of records in the source and target tables.
- Compare the data types and data lengths in the source and target tables.
- Compare the column names in the source and target tables.
- Compare the constraints in the source and target tables.
- Compare the date format in the source and target tables.
- Check for duplicate records in the target tables.
- Check for irrelevant and bad data in target tables
- Check for transformation logic is applied as per mapping on the target table columns from source table columns.
i.e., we will create a SQL query for below business rule and test the data

- Comprehend the Business Logic: Initially, we will grasp the underlying business logic and formulate a query in accordance with the Business Rule.
- Apply the Business Rule: The Business Rule dictates that the FULLNAME attribute from the PURCHASER source table will be divided into substrings at each space. The first substring of FULLNAME will then be transferred to the FIRST attribute of the CUSTOMER_DIM table.
- Execute the Transformation: This transformation will be applied to all the data present in the FULLNAME attribute of the PURCHASER table.
Query for this will be as:
Source table query: Select FULLNAME from PURCHASER
Target table query: Select FIRST from CUSTOMER_DIM - Compare and Validate the Results: We will compare the results obtained from the source and target tables. We will verify that the query on the target table returns data within the FIRST attribute. This data should consist solely of the first name, represented as a single string.
Pros and Cons of ETL Testing
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) testing has several advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages:
- Error Identification: ETL testing helps identify errors in the ETL process, ensuring data accuracy.
- Data Validation: It validates data transformation.
- Maintenance and Traceability: ETL tools make maintenance and traceability much easier than hand-coding⁴.
- Suitable for Data Warehouse Environment: ETL is good for bulk data movements with complex rules and transformations, especially in a data warehouse environment.
Disadvantages:
- Time-Consuming: ETL testing can be time-consuming.
- Expensive: It can be expensive.
- Requires Specific Skills: ETL testing requires people with different and specific skills.
- Batch Mode Limitation: ETL tools typically aren't that great at near-real time or on-demand data access. They were geared towards more of a batch mode of working.
- Limited User Accessibility: ETL is an IT tool that's not accessible to data analytics and business users directly.
- Requires Data Oriented Developers or DBAs: You must be a data-oriented developer or database analyst to use ETL tools.
Please note that the pros and cons can vary based on the specific ETL tool being used and the complexity of the data and transformations involved.
Why Is ETL Testing Still Necessary?
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) testing is necessary for several reasons:
Data Quality Assurance: ETL testing ensures that the data transferred from heterogeneous sources to the central data warehouse is accurate, complete, and reliable. It prevents data errors and preserves data integrity.
Business Decision Making: Without ETL testing, businesses run the risk of making decisions using inaccurate or incomplete data. This can have negative impacts on revenue, strategy, and customer experience.
Cost Savings: According to a Gartner report, organizations lose around 15 million USD annually due to poor data. ETL testing helps avoid such losses.
Compliance with Transformation Rules: ETL testing ensures that data transfers happen with strict adherence to transformation rules and compliance with validity checks.
Early Error Detection: The process also helps in the early detection and mitigation of defects and errors.
In summary, ETL testing is crucial to ensure high data quality, which is vital for analytics, business intelligence, and decision-making.
Conclusion
ETL testing is a very critical phase for data warehousing projects as it provides the construction, management and security of integrated data or migrated data. This process achieves the validation, verification and qualification of data, effectively preventing data loss and duplication of records. It makes sure that the data extracted from multiple sources and loaded into the data warehouse is correct. Overall, ETL testing is different from database testing in terms of its scope and the steps followed during this testing.
Ensure your data pipelines run smoothly with PixelQA, your go-to software testing company. Leverage our expertise in ETL testing and unlock the full potential of your data infrastructure. Reach out now for a consultation tailored to your needs!
About Author
 Hardik Mochi started his testing journey in October 2015 as a Junior Software Tester, and now he is an Associate Team Lead at PixelQA. With a focus on testing mobile apps, Windows applications, and web portals in the RX and CG domains, Hardik developed strong software testing skills. Progressing to Senior Tester over 5.5 years, he transitioned to XDuce India PVT LTD, specializing in ETL testing and acquiring SQL expertise, complemented by earning the AZ-900 certification. He is eager to delve into automation while maintaining interests in electronic hardware, current affairs, and geopolitics, aiming to advance as an automation professional in the future.
Hardik Mochi started his testing journey in October 2015 as a Junior Software Tester, and now he is an Associate Team Lead at PixelQA. With a focus on testing mobile apps, Windows applications, and web portals in the RX and CG domains, Hardik developed strong software testing skills. Progressing to Senior Tester over 5.5 years, he transitioned to XDuce India PVT LTD, specializing in ETL testing and acquiring SQL expertise, complemented by earning the AZ-900 certification. He is eager to delve into automation while maintaining interests in electronic hardware, current affairs, and geopolitics, aiming to advance as an automation professional in the future.


