
Selenium has significantly transformed the landscape of automating web applications across browsers and platforms. However, starting a Selenium automation project does not just mean coding. One other aspect of setting up a project is dependency management, especially for whatever dependencies are in the pom.xml file of a Maven-based project. This article concentrates on the standard dependencies that generally go into pom.xml for Selenium automation and their relevance in Selenium Automation Testing Services, as well as beyond in test automation.
In the end, to link dependencies into the pom.xml file is to ease dependency management and project maintainability and enrich the process of development within a Maven-based project for test-automation services.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Dependencies in `pom.xml` for Selenium WebDriver Projects
- Steps to Add Dependencies in Maven's `pom.xml`
- Dependencies Overview and Download Links
- Distinguishing Between Incorporating Maven Dependencies vs. Manual JAR Integration
- Challenges and Considerations in Maven's Dependency Management
- Optimizing Maven Dependency Handling
- Conclusion
Understanding Dependencies in `pom.xml` for Selenium WebDriver Projects
What is `pom.xml`?
The `pom.xml` file is a kind of definition file in Apache Maven projects that specifies the project features and the dependencies and the build details. It is so important for managing the configuration and dependencies of a project in Maven.
What are dependencies in a `pom.xml`?
These files are necessary to support the Selenium framework in a Maven project for Selenium WebDriver projects. These all dependencies include their group ID, artifact ID, and version in the pom.xml which will then resolve through Maven, automating library management for test automation with Selenium WebDriver, because everything is already compatible and functional.
Understanding dependency structure entails recognizing three integral parts within XML syntax -
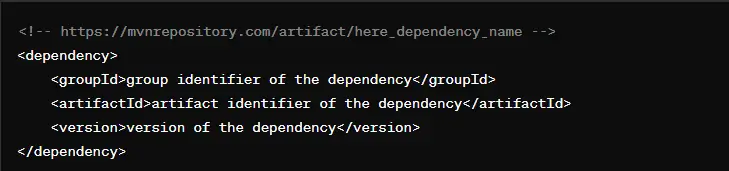
- groupId: The `groupId` (Group Identifier) is a unique identifier for a project or a set of artifacts. It typically follows the reverse domain name notation (for example, `com.example`).
- artifactId: The `artifactId` is the name of the specific artifact (to be JAR, WAR, etc.) being referred to. Usually, this is the name of the project or module without any version information. For example, in case of a project named "my-project," the `artifactId` can also be "my-project".
- version: This element indicates the version of the dependency that will be used by the project.
Steps to Add Dependencies in Maven's `pom.xml`
Navigate to Maven Repository: Go to Maven Repository webpage to view.
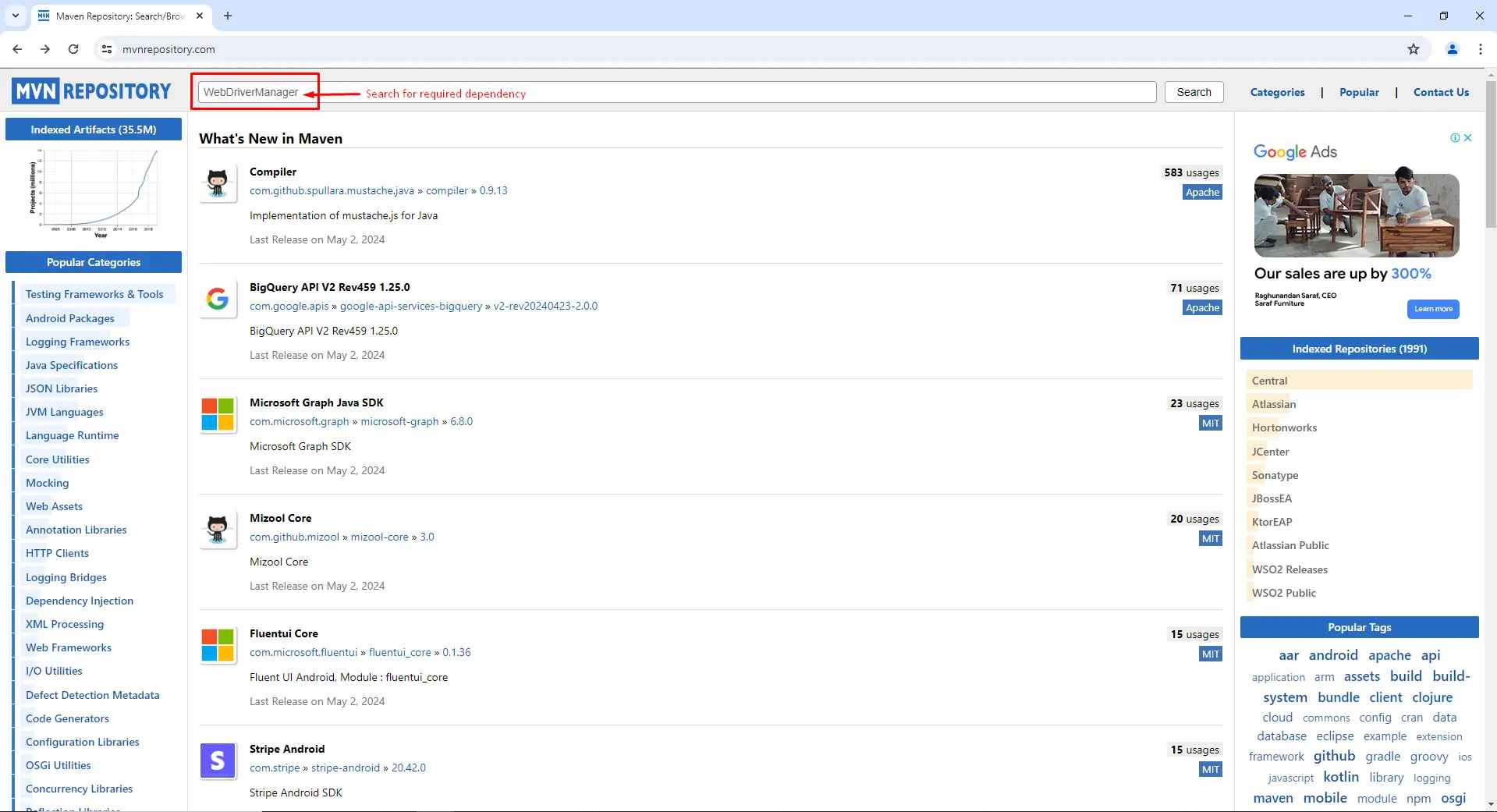
Search for Dependencies: For your project, use the search box to locate the dependencies you need. For ex- WebDriverManager
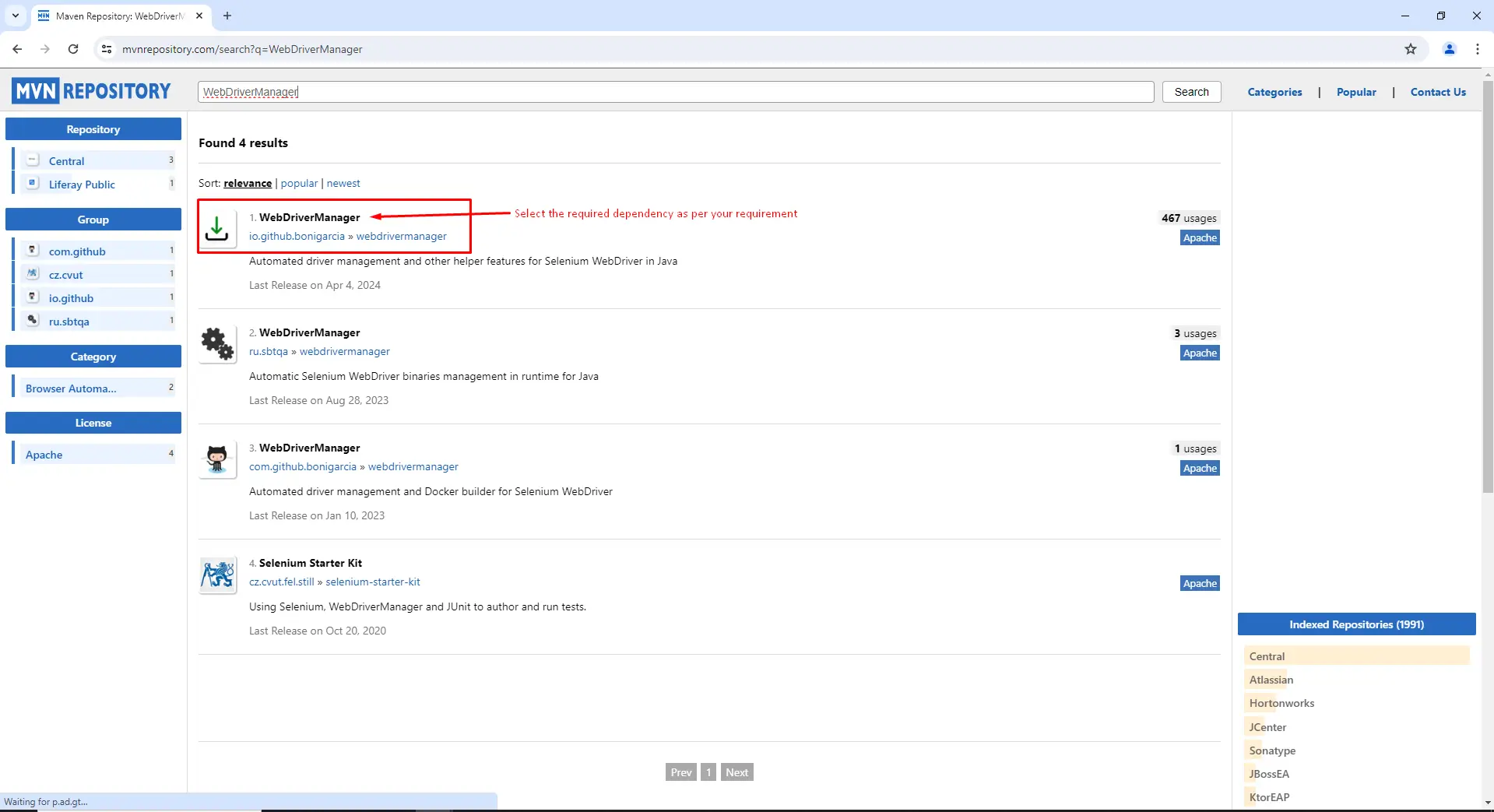
Select Dependency: Click on the desired dependency from the search results.
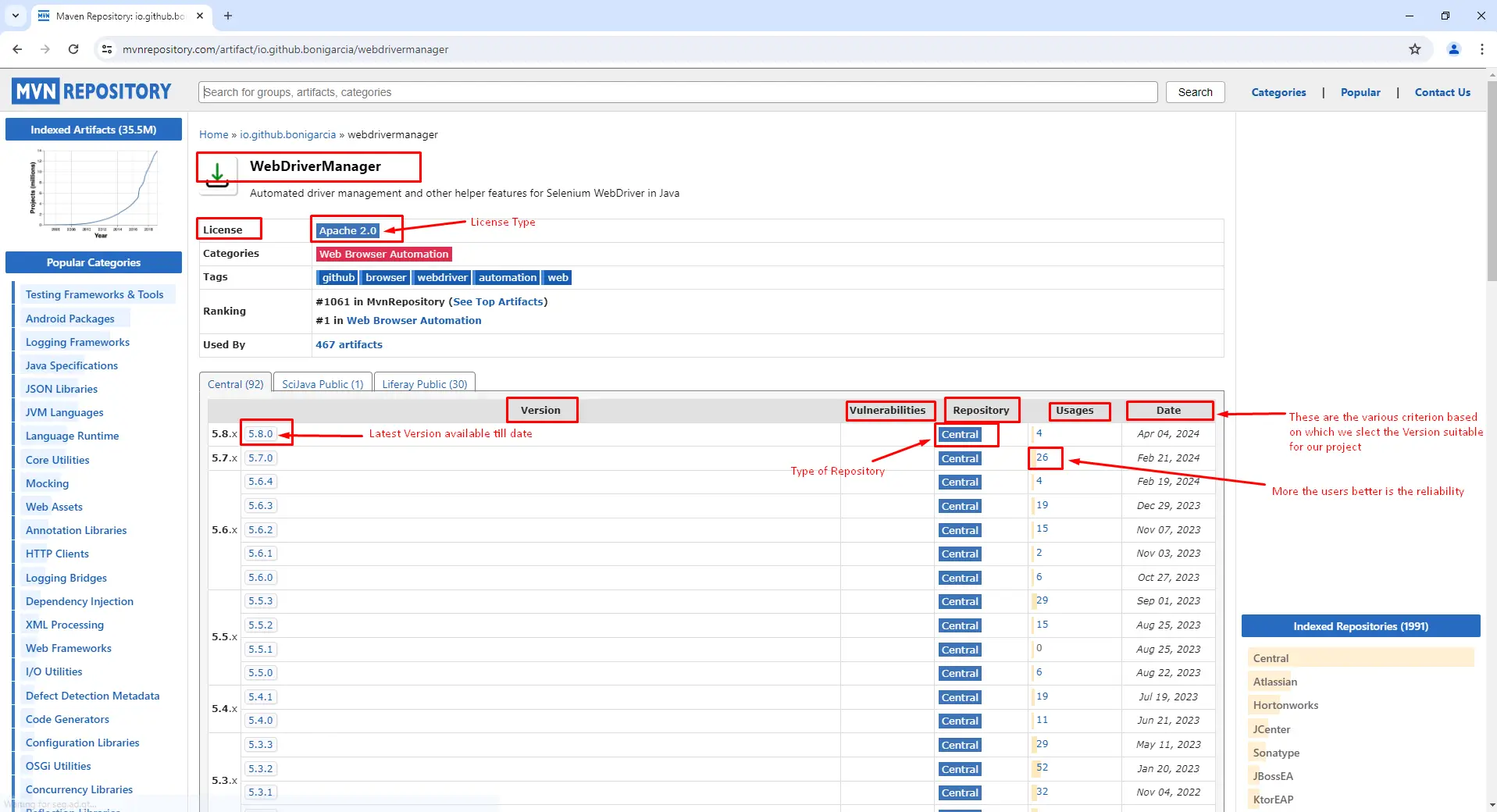
Choose Version: Consider the factors listed below to select the appropriate version.
- Date - The date when the dependency was published.
- Vulnerabilities - Potential vulnerabilities associated with the specific dependency.
- Usage - The number of users indicates the level of downloads.
- Types of repositories - Local Repository, Central Repository, Remote Repository, Proxy Repository, Repository Groups, and Custom Repositories.
- Types of licenses - Apache License, GNU General Public License (GPL), MIT License, Mozilla Public License, Eclipse Public License, Creative Commons Licenses, and Proprietary or Commercial Licenses.
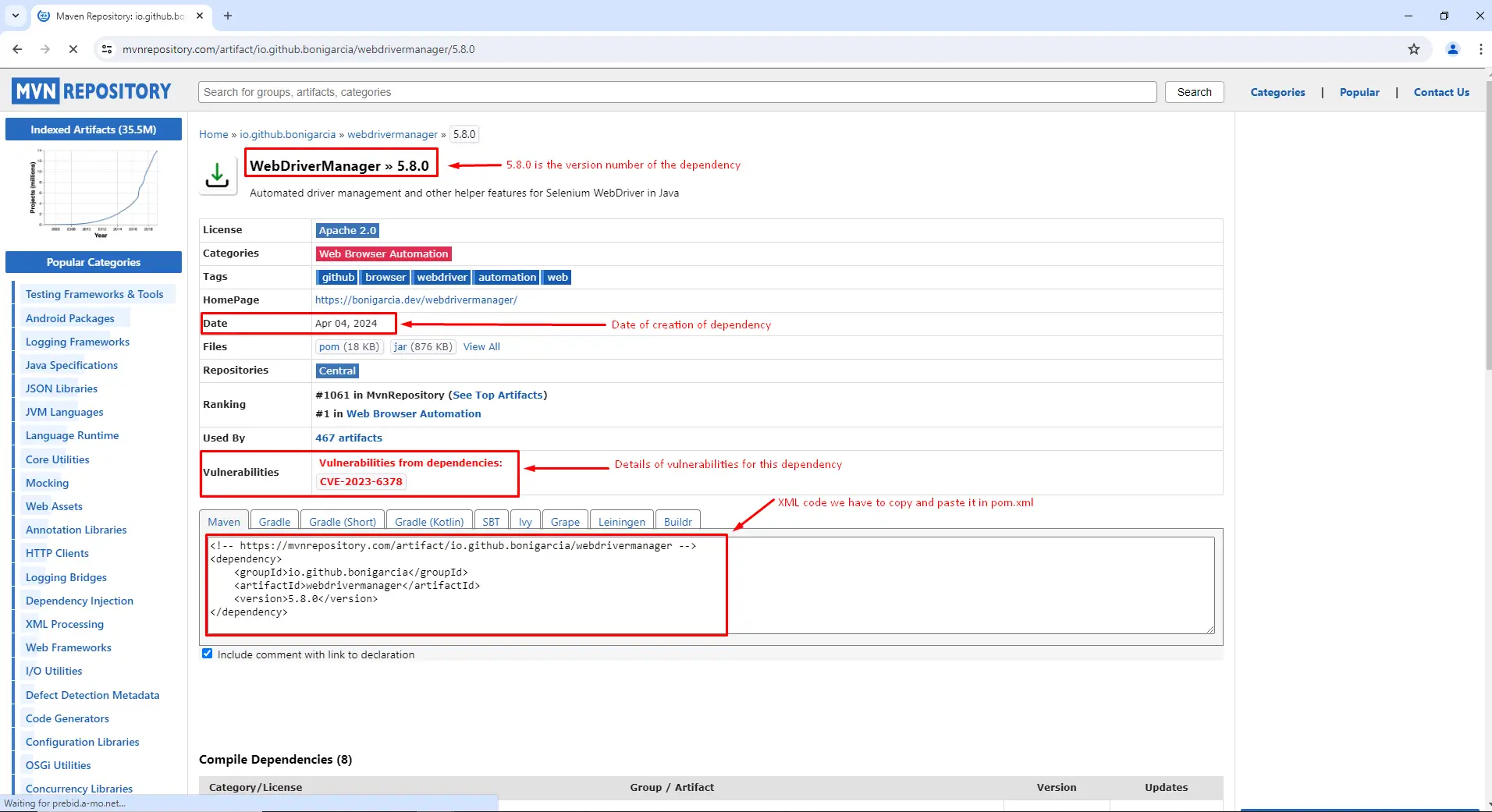
Copy Maven XML Code: Copy the XML code provided on the dependency's page. This code typically includes the `<dependency>` block with the group ID, artifact ID, and version.
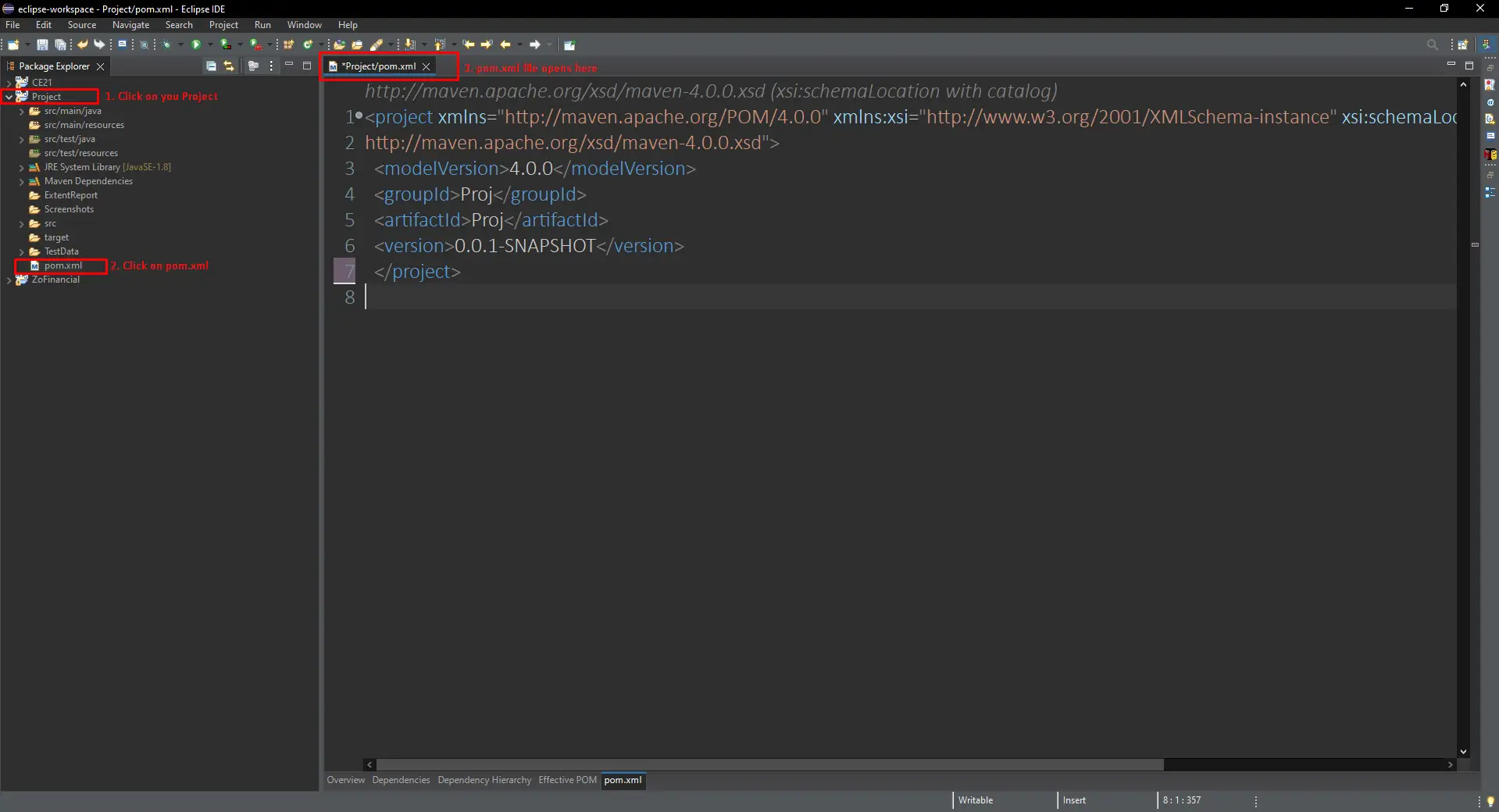
Navigate to Project's pom.xml: Open your Maven project's `pom.xml` file.
Paste Code into Dependencies Section: Locate the `<dependencies>` section within the `pom.xml` file and paste the copied XML code inside it.
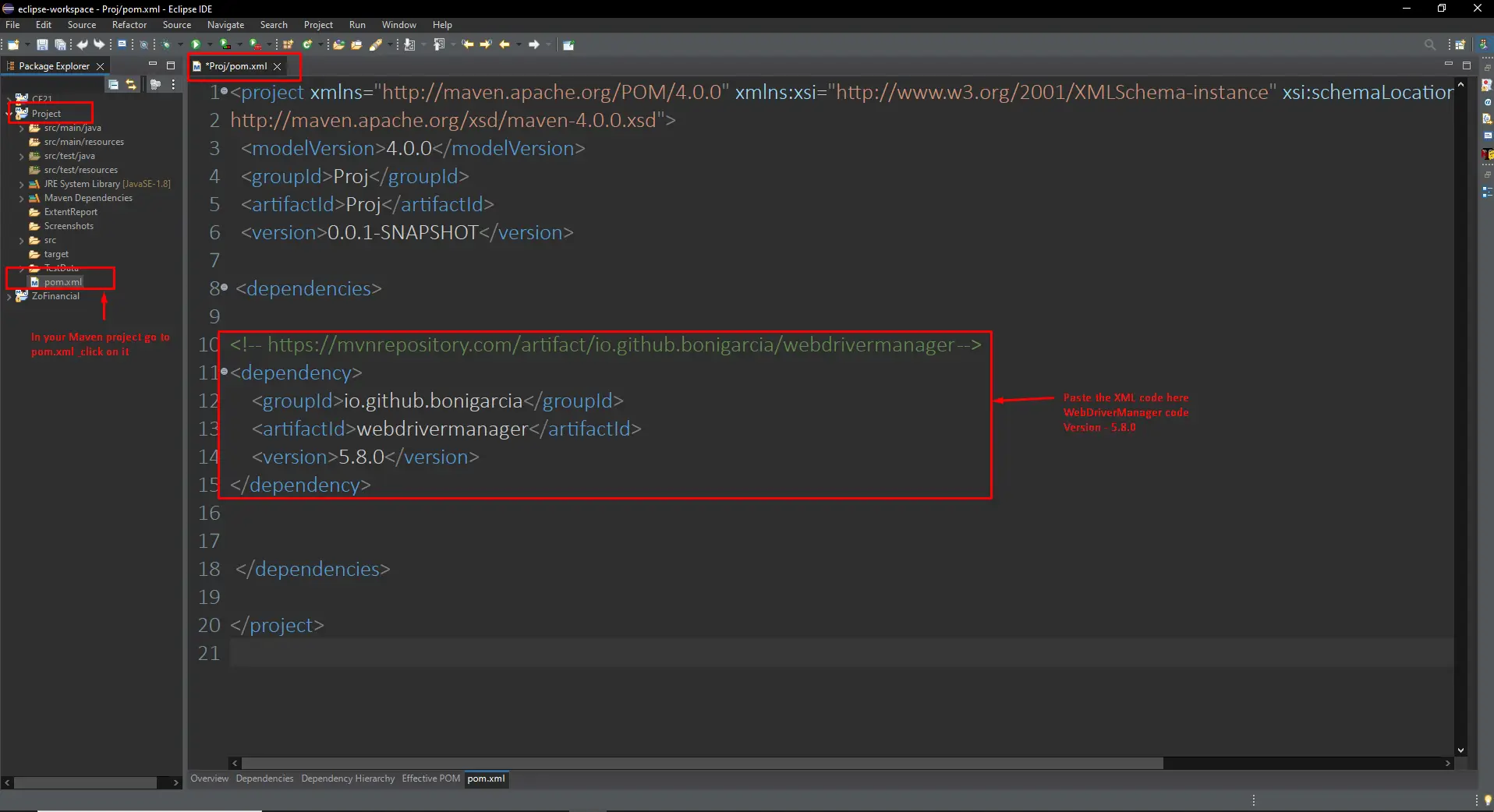
Save Changes: Save the `pom.xml` file to apply the changes to your project.
Dependencies Overview and Download Links
| Sr no. | Dependency | Description |
| 1 | Selenium WebDriver Dependency | This dependency offers the essential APIs needed to interact with web elements across various browsers. |
| 2 | WebDriverManager Dependency | The WebDriverManager dependency facilitates the management of browser-specific drivers essential for programmatically controlling browsers. |
| 3 | Automation testing require a robust testing framework to effectively organize and execute your tests. Popular options include JUnit and TestNG. | |
| 4 | Log4j Logging and Extent Reports Dependencies | Logging and reporting are essential for tracking test execution and debugging failures. Dependencies like Log4j and ExtentReports can be added for this purpose. |
| 5 | Apache POI Common and POI-OOXML Dependencies | Apache POI serves as the elemental library for Java-based control of Microsoft Office reports. Moreover, POI-OOXML, a component of Apache POI, specializes in supporting Office Open XML (OOXML) designs utilized by modern Microsoft Office applications. |
| 6 | dependency | It offers tools for typical input/output tasks in Java, like reading, writing, copying files, and managing streams. |
| 7 | Apache Velocity dependency | It's a versatile template engine that simplifies dynamically generating text content in Java applications, like HTML, XML, or any other formatted text. |
| 8 | MS SQL JDBC dependency | This dependency allows Java Testers to establish database connections, send SQL queries, and process query results within their Java applications. |
| 9 | This plugin enables you to customize compiler settings in your Maven project, like setting Java version compatibility, toggling compiler warnings, and more. |
Challenges and Considerations in Maven's Dependency Management
Overhead in Dependency Management: Handling dependencies by hand can be laborious, particularly for big projects with many of dependencies.
Dependency Conflicts: When various dependencies call for incompatible versions of the same library, dependency conflicts may arise.
Version Compatibility: It can be challenging to make sure dependencies are compatible, particularly when interacting with other frameworks or libraries. Carefully choosing compatible versions of dependencies is necessary for developers to prevent unexpected behaviour or runtime issues.
Dependency Bloat: Dependency Bloat is the production of a great many or even unwanted dependencies that make a project larger and much more complex than it need to be, resulting in longer build times, and more resource usage.
Dependency Security: Requirements that come from outside sources could include libraries that are known to have security flaws.
Optimizing Maven Dependency Handling
The methodical approach and analysis of typical problems in Maven projects lead to fixing the dependency resolution problems.
Check Dependency Versions: All dependencies must be compatible with one another. (You will need an issue with the Maven dependency:tree command to visualize the dependency tree to troubleshoot conflicting versions).
Review Maven Output: Maven typically provides helpful information about conflicts, missing artifacts, and resolution strategies. Look for error messages or warnings indicating issues with dependency resolution.
Inspect Maven Repositories: Make sure the artifacts it needs are in the remote repositories specified in your project's `pom.xml`. Artifacts can occasionally go missing due to a temporary network or server problem. Use the `-U` (update) flag of Maven to force the updating of snapshots and releases from the remote repositories.
Use Maven Central Repository: Make sure that the main repository you use to download dependencies is the Maven Central Repository.
Excluding Transitive Dependency: If there are conflicts or compatibility issues due to transitive dependencies, a transitive dependency may be excluded from a Maven project via `exclusions` defined in the `pom.xml`.
Update Maven and Plugins: Ensure that the necessary plugins and Maven are updated to the latest version.
Use Dependency Management Tools: Leverage dependency management tools such as Apache Ivy, Gradle, or use IDE plugins like IntelliJ IDEA's dependency analysis to aid in the resolution and management of dependencies for your project.
Conclusion
Managing Selenium dependencies through 'pom.xml' in Maven is crucial for efficient project setup and maintenance. This blog has emphasized the importance of dependency management, highlighted essential Selenium dependencies, and discussed Maven's role in automating dependency resolution. By leveraging Maven's capabilities, developers can streamline Selenium automation projects, reduce overhead, and ensure project scalability. Despite challenges like dependency conflicts, Maven offers robust solutions to enhance project stability and efficiency. A Software Testing Company can help teams adopt proactive dependency management practices, empowering developers to utilize Maven effectively in contemporary software development processes.
So, are you looking for top-notch Selenium testing services? Yes! Look no further. Partner with the best software testing company today to optimize your automation projects and ensure superior software quality.
About Author
 Shubham Wadhai is a focused Test Analyst at PixelQA with a solid grounding in software testing methodologies and technologies. The man started his career as a professional in the year December 2021. He shot up to coordinate end-to-end testing agilely across domains such as Healthcare, Edtech, and eCommerce, quickly moving from manual testing, which was done by specialists. Transitioning to automation, he writes tests using Java and Selenium with an emphasis on the efficiency and accuracy of the process. For now, the focus is on getting ISTQB certification and learning advanced technologies for excelling in non-functional testing while contributing enthusiastically to innovative PixelQA projects.
Shubham Wadhai is a focused Test Analyst at PixelQA with a solid grounding in software testing methodologies and technologies. The man started his career as a professional in the year December 2021. He shot up to coordinate end-to-end testing agilely across domains such as Healthcare, Edtech, and eCommerce, quickly moving from manual testing, which was done by specialists. Transitioning to automation, he writes tests using Java and Selenium with an emphasis on the efficiency and accuracy of the process. For now, the focus is on getting ISTQB certification and learning advanced technologies for excelling in non-functional testing while contributing enthusiastically to innovative PixelQA projects.



