
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Selenium Automation Testing
- Architecture of Selenium 3 vs Selenium 4
- Selenium 3 vs Selenium 4: Core Differences
- Comparison Table: Selenium vs Selenium 4
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
As technology matures, it is very necessary for software testers and developers to be aware of the latest tools and techniques. Among other things, Selenium, the world's most popular open-source framework for automated testing, has improved web application testing. A number of enhanced and new features in Selenium 4 really can augment the efficiency of automated testing services.
So in this article, we will have a detailed overview of Selenium 3 vs. Selenium 4 differences, primarily innovations and their improvements. We will try to evaluate the enhanced functions and advanced features and their overall effect on the automation testing process.
What is Selenium Automation Testing?
Selenium Automation Testing is a very famous software testing framework used for automating web applications. It allows testers to create test scripts that are run on a variety of platforms and browsers in a variety of computer languages. Testers can basically verify the functioning and behavior of web applications while simulating the actual user interactions with Selenium, such as clicking a button, typing some text, and moving from one web page to another.
The capability of SA Testing to execute test scripts on a range of browsers is one of its key features. This ensures a smooth user experience by having the web application behave consistently. Across different browsers. Also, it provides parallel execution. This reduces testing time by allowing testers to execute multiple test cases simultaneously. Selenium Automation Testing has emerged as an essential tool in the software testing field. Because of its stable and flexible design. It allows companies to develop correct and high-quality web applications efficiently.
Architecture of Selenium 3 vs Selenium 4
Let's have a look at Selenium 3 and Selenium 4 architecture. Unveiling advancements that enhance test automation efficiency and compatibility.
Selenium 3 Architecture:
This architecture follows a client-server model. This is how it breaks down: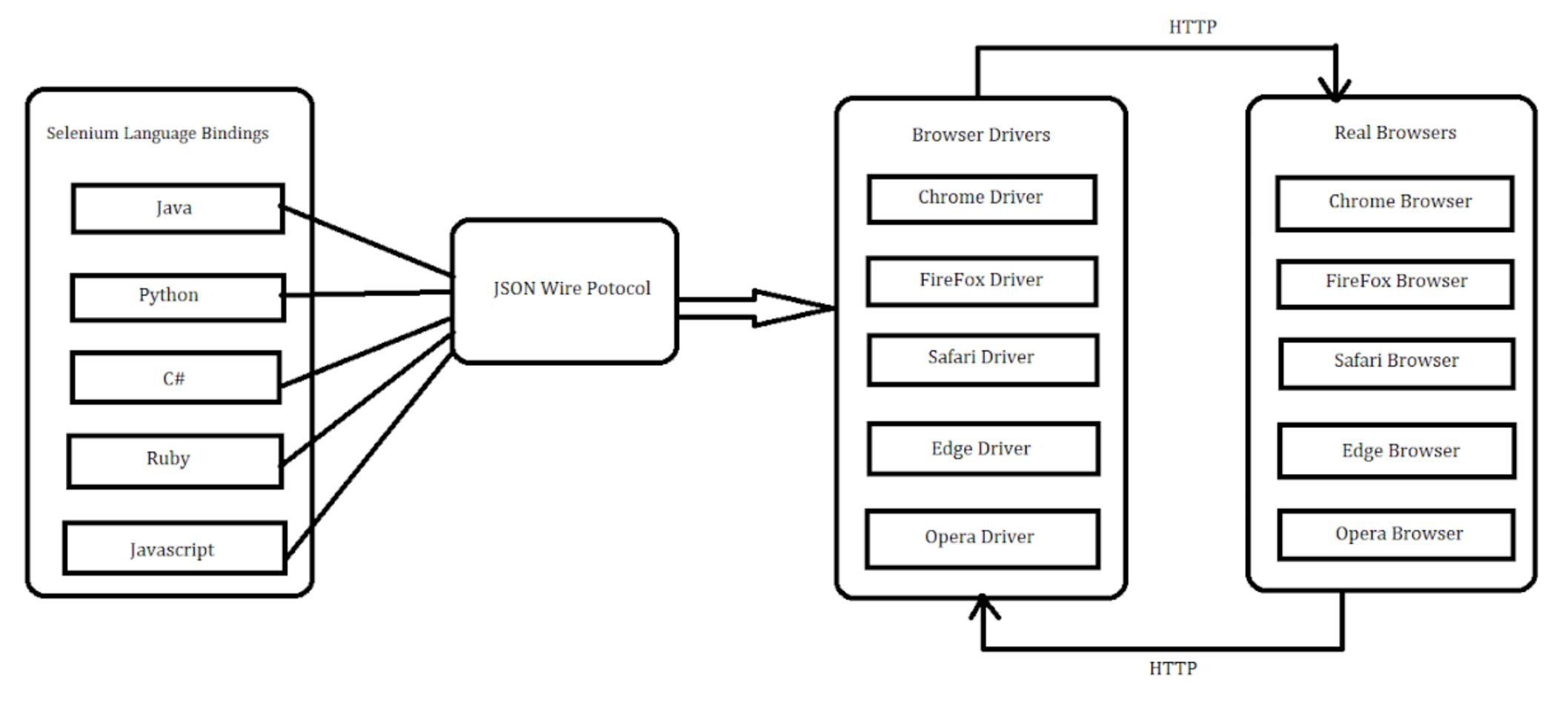
1. WebDriver API: The Dependency of Selenium 3 is mainly on the WebDriver API. It offers a platform-independent interface to automate them for direct interaction with the web browser. In contrast to Selenium RC, the API is designed to be much simpler and unsophisticated.
2. Browser Drivers: Selenium 3 utilizes drivers for interacting with different web browsers. The drivers act as a bridge between the automated browser and the WebDriver API. Each of these drivers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, etc.) is required so that WebDriver can direct the behavior of these browsers.
3. JSON Wire Protocol: Selenium 3 utilizes the JSON Wire Protocol as a vehicle of communication between the WebDriver client libraries (such as Java and Python) and the WebDriver server. It is a standardized mechanism of sending data in both directions and thus simplifies integration between various versions of browsers as well as programming languages.
4. Selenium Server: In Selenium 3, the client library and the drivers communicate via the Selenium Server. It allows communication between the client and the WebDriver. Instances that are running on several computers, and it maintains multiple browser sessions.
Selenium 4 Architecture:
The core of the Selenium 3 design is a client-server distributed testing platform. Here is a thorough synopsis: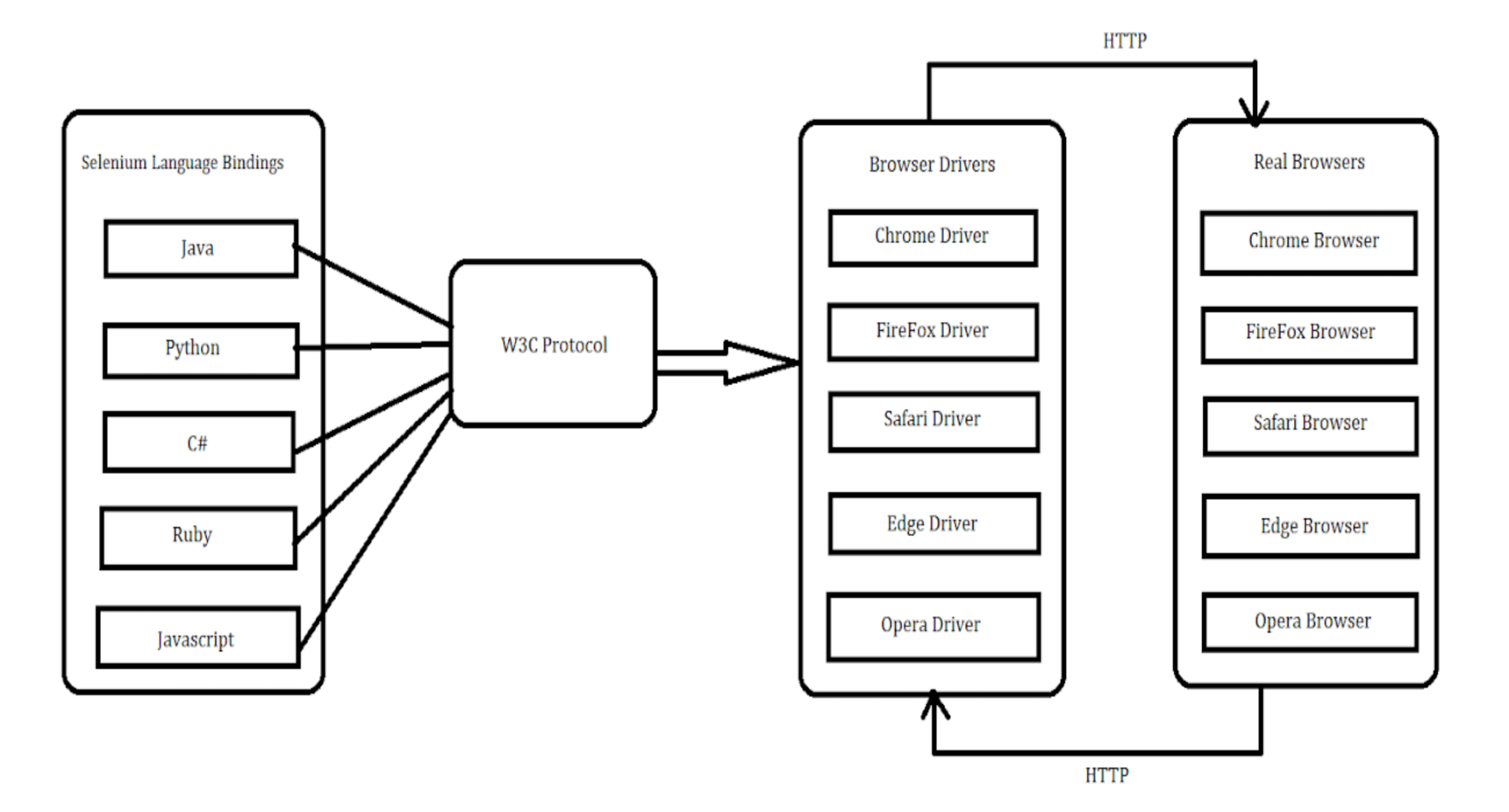
1. WebDriver API: It offers a common method for automating web browsers and forms the core part of Selenium 3. By utilizing this API, users can automate activities, interact with web elements, and scrape data from web pages in code. WebDriver simplifies the automation of tests by providing a common set of commands that could be used in most browsers.
2. Browser-Specific Drivers: In order to assist the WebDriver API in communicating with various web browsers, Selenium 3 employs browser-specific drivers. They serve as intermediaries, translating WebDriver commands into action. In order to enable Selenium to support numerous browsers, there are various drivers for popular browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, and Safari.
3. JSON Wire Protocol: To allow WebDriver servers and client libraries to get along, Selenium 3 uses the JSON Wire Protocol. This is a standard method of data transfer, which allows for simple interaction irrespective of programming language or implementation. By creating a set of HTTP endpoints for sending commands and receiving responses, it offers consistency and compatibility.
4. Selenium Server: The central part of the Selenium 3 system is the Selenium Server. It enables WebDriver instances and client libraries to talk to each other by handling browser sessions. It is also a central place for running tests on different web browsers and machines so that you can run tests at the same time. Whether you install the Selenium Server on your machine or another machine depends on your test requirements.
5. Remote WebDriver: Additionally, Selenium 3 allows for remote WebDriver instances, which allows tests to be conducted on distant computers or devices. In testing multiple environments and configurations, the feature is very useful in distributed testing. Cross-platform testing can be performed by teams and resources can be utilized efficiently through the use of Remote WebDriver, without the need for physical access to every target device.
6. Selenium Grid: A distributed framework for running tests concurrently on many nodes and environments, Selenium 3 works well with Selenium Grid. You can create a WebDriver server grid using Selenium Grid. All such servers are able to run tests across various operating systems and browsers simultaneously. This form of testing is best suited for large automation projects since it accelerates running tests and makes tests more efficient.
Selenium 3 vs Selenium 4: Core Differences
Comparing Selenium 3 vs 4, The following are the main variations between the two versions:
1. Chrome Driver
The Chrome Driver extension will be the main difference between Selenium 3 and 4. In Selenium 3, the Chrome Driver is extended to the Remote Web Driver. However, Chrome Driver is an extension of the Chrome Driver Class in Selenium 4.
2. Communication Mode Between Client and Server
As seen from the design of Selenium 3 and 4, Selenium 3 features a JSON Wire Protocol that allows data to be exchanged between the client and the server.
On the other hand, since Selenium 4 uses the WebDriver W3C protocol to establish communication between the client and server, JSON Wire Protocol is not needed in this scenario.
3. Selenium Grid: From Selenium 3 to 4
Version 4 of Selenium Grid features a redesign focused on scalability and user-friendliness. It may now be used more successfully for distributed testing, enabling the simultaneous execution of tests across many environments and browsers, and it provides enhanced load balancing.
Apart from this, it facilitates easier configuration, improved logging, and Docker containers. Improved capabilities to execute tests in parallel across various settings and configurations, increasing the efficiency and speed of test execution.
4. Start of Node and Hub Bars
To perform automation testing in Selenium 3, testers must always launch the Hub and Node jars. It can get challenging at times for the testers. With Selenium 4, testers can eliminate these kinds of issues because automation testing can be carried out without launching the Hub or Jar.
5. Backward Compatibility and Transition
Another feature of Selenium 4 is that it is backwards compatible with Selenium 3 so that customers can upgrade easily and with minimal changes to their existing test scripts. Several old features and methods from its predecessor, Selenium 3, are deprecated in Selenium 4 to encourage users to use the newer and more efficient ways.
Comparison Table: Selenium 4 vs Selenium 3

Conclusion
The Selenium 3 to 4 upgrade is a major step in web testing, especially for teams leveraging Software Testing Company. Selenium 4 is faster on multiple platforms and is effective by utilizing the W3C WebDriver standard, thus no extra servers are needed. Testers now possess better and easier tools because of new functionality like relative locators, Chrome DevTools Protocol integration, and better window and tab handling.
This latest version has made it clear in its communication with earlier versions that you can easily upgrade to the latest version without major interruption of your test scripts- previous users can begin taking advantage of the new features without any significant disruption to the test scripts. The newer version of Grid is now much better suited for parallel testing and enables better scaling and management of tests in other contexts.
The structure of the whole thing to be latest improved, to bring testers and developers experience closer to that smooth, stable, and simplified touch of modernity. With the new functionalities of Selenium 4, it makes up for being the right option to keep pace with newer or redeveloping automation projects, based on the increasingly changing spectrum of web automation today.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the most significant differences between Selenium 3 and Selenium 4?
Selenium 4 has numerous enhancements from the older version. It supports the W3C WebDriver protocol, has improved browser driver support, support for the Chrome DevTools Protocol, relative locators, improved window and tab handling, and a new Selenium Grid with simplified parallel testing.
2. What is the need for the W3C WebDriver standard in Selenium 4?
The W3C WebDriver standard allows talking easily to web browsers so that they can talk back to each other faster and better. For this reason, Selenium 3 uses the JSON Wire Protocol less and therefore achieves more correct and stable results across different browsers.
3. In what ways does Selenium 4 improve browser support compared to Selenium 3?
Selenium 4 now provides built-in, more stable and efficient browser drivers for browsers like that, launched newly, called Microsoft Edge, and based on Chromium. Improvement in performance, offer of new features, improvements in compatibility with newer web technologies of these improvements clearly seem to have been made over that.
4. What are relative locators, and how do they enhance testing using Selenium 4?
The relative locators in Selenium 4 help a user in finding elements with respect to other elements in which it is located (for example, above, below, to the left, to the right). This facility makes it easier to refer to the elements, thus making it easier to read and record test scripts.
5. Should I upgrade to Selenium 4 if I am presently using Selenium 3?
There are several new features in Selenium 4, and upgrading is quite a good option. You can use Selenium 4 for both fresh and old automation projects as further browsers are supported and have more advanced features and a more streamlined test environment without it contradicting the previous version.
6. What types of applications can you automate with Selenium?
Actually, testing automation exists for countless web applications, including online stores, content management sites, business apps, and custom sites. Selenium supports all major browsers and thus makes testing cross-browser operable.
7. Do you offer tailored test automation frameworks?
Yes. We design tailored test automation frameworks that meet your unique needs and requirements. We make our frameworks simple to extend, simple to maintain, and simple to use so that you can attain effective and efficient test automation.

