Introduction
APIs form the backbone of all modern software due to their capacity for the seamless transfer of communication between software components across the development. The increased usage of APIs necessitates their optimal functionality, reliability, and security. Here's where API testing services come into play.
Manual testing has traditionally been performed with much time and effort for conducting repetitive tests and validating complex scenarios. With automation in place, businesses tend to put in place measures that will assure overall software quality, speed up their release cycles, and make testing much more flexible.
Table Of Contents
- What is API testing & how is it different from other types of testing?
- Why Automated API Testing?
- Types of API Automation Testing
- How to Automate API Testing?
- Challenges of Automation API Testing
- Conclusion
What is API Testing and How is it Different from Other Testing Types?
API testing is important in software development for checking functionality, performance, security, and reliability. Unlike GUI testing, which tests the application's user interface, it tests the application by talking with backend services. Testing verifies that APIs can handle failures, behave as expected, return valid responses, and maintain integrity with data throughout operations. By performing API testing at the early stages before full UI readiness, developers can detect problems early and make sure their systems are healthy across various platforms and environments.
Such an approach provides a fast feedback loop, allowing issues to be spotted and resolved early enough to avoid impacts on other system components. This is critical for ensuring interoperability and communication among the software components and services present in a complex ecosystem. Quality and scale are further enhanced by focusing on API-enabled core functionalities that make any application changeable and scalable for future improvements.
Why Automated API Testing?
Automated API testing has become a crucial part of current software development, promising reliability and robustness in the application on validation of different components interactions. It saves developers from manual, time-consuming human error associated with testing and has simpler provisions for consistent and rapid execution of test cases with timely feedback about functionality and quality against accelerated issue identification and an enormously reduced chance of defective production. In the end, a better user experience will be possible through delivering more dependable and stable software.
Automated API testing is also an important contribution to efficiency and scalability in the QA process. It allows the executing of a large number of test cases easily across different environments and configurations. Embedded into the CI/CD pipeline, such tests guarantee that any new code changes will not compromise existing functionality, thus facilitating faster and more reliable product releases. Finally, with increased test coverage at lower costs and shorter development cycles, businesses will be able to push more frequent, more dependable software releases into production.
How to Automate API Testing?
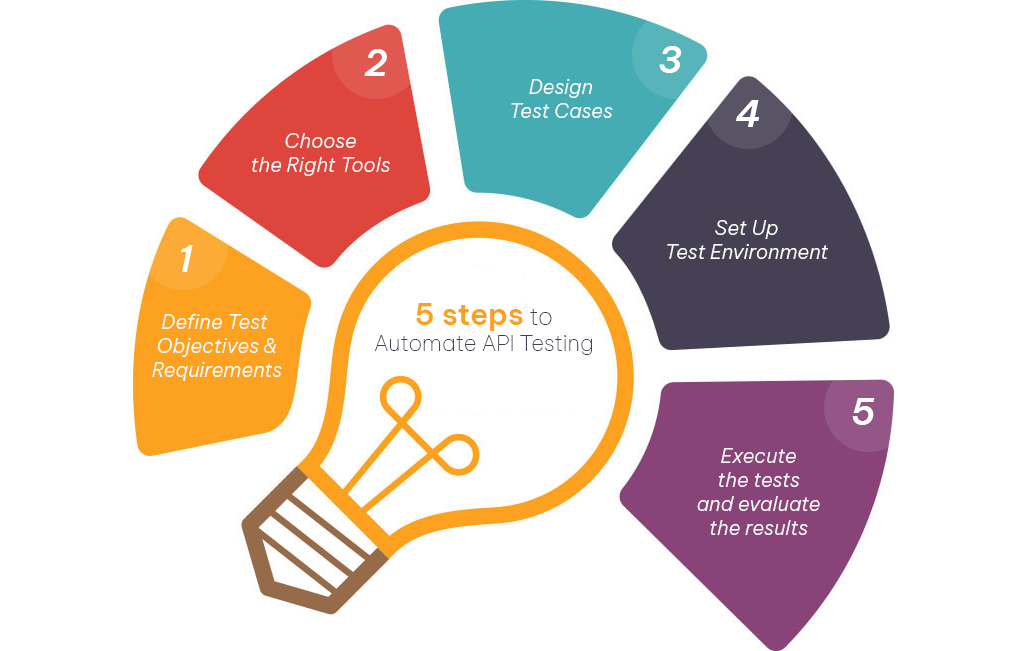
1. Define Test Objectives and Requirements
In order to initiate the process, a listing of all API endpoints that have to be tested should be created, together with test scenarios and edge cases, which must involve expected replies and valid and invalid requests. In order to make the testing process comprehensive and efficient, it is important to agree on certain objectives such as establishing data integrity, performance, security, and error handling. This will help to align team efforts.
Although the criteria will always depend on the specifics of the project, the following are the most common ones:
- What defines a passed or failed test
- What the team aims to achieve through testing
- Whether and how it interacts with other APIs
- The API's primary and secondary functionalities
- What the API is intended to do and for whom
2. Choose the Right Tools
Achieving successful API automation requires careful consideration of the test frameworks and tools chosen. Popular options with lots of functionality for its testing include Postman, SoapUI, RestAssured, or JUnit. To enable this throughout the process, it's also critical to confirm that these technologies can easily interface with your CI/CD pipelines, such as Jenkins, GitLab CI, or Travis CI.
3. Design Test Cases
One of the most important steps while hiring API testing services is creating thorough test cases. Writing test scripts that include the request method, URL, headers, arguments, and anticipated responses must be done for every API endpoint and situation. Ensuring that it appropriately reflects real-world usage and conditions also requires preparing and managing test data, whether it is created dynamically or statically.
4. Set Up Test Environment
For testing to be dependable and consistent, the test environment must be configured correctly. This entails configuring many settings, including production, staging, and development, and making sure that the API endpoints are appropriately set up for each. Controlling environment variables facilitates smooth transitions between environments and speeds up the testing process. Examples of these variables include authentication tokens, endpoints, and API keys.
5. Execute the tests and evaluate the results
This is the phase in which you assess not only the API's quality and stability but also the accomplishment of the earlier project planning stages. Testers can choose to run tests in parallel to improve performance and decrease dependency. They can use one or more API automation testing tools to analyze the test results.
Types of API Automation Testing
1. Validation Testing
The main goal of validation testing is to confirm that the API satisfies its requirements and operates as anticipated in typical scenarios. It guarantees accurate generation of outputs, proper processing of inputs, and compliance of the API answers with pre-established contracts or standards. It consists of:
- Protocol Validation: Checks compliance with the HTTP/HTTPS protocol and other communication standards.
- Data Validation: Verifies the completeness and accuracy of the data that the API returns.
- Schema validation: It is the process of making sure API answers follow the specified data schema.
2. Functional Testing
Through evaluating different inputs, outputs, and functionalities, functional testing verifies the functional operations of API endpoints. It focuses on managing various use scenarios, making sure all anticipated capabilities execute as planned, and accurately answering both legitimate and incorrect requests. Important elements of this type of testing consists of:
- Error Handling: Examining how it handles and responds to exceptions and errors.
- Parameter Testing: Checking how the API's handles various parameter values.
- Endpoint Testing: Its individual API endpoints are used to verify their functionality.
3. Security Testing
The goal of this testing type is to find holes and flaws in the API that could be used by bad actors. Testing for typical security risks like these is part of it.
- Injection Attacks: Checking vulnerability to exploits such as SQL injection or cross-site scripting (XSS) to compromise data integrity or leak sensitive information.
- Data Integrity: Ensuring that the data received via the API is encrypted and secured from tampering.
- Authentication and Authorization: Ensuring that access controls are correctly implemented and enforced.
4. Load Testing
An API's scalability and performance under typical load situations are evaluated. The procedure embraces the emulation of several concurrent users or transactions in order to analyze the response time, throughput, and resource utilization by the API at different loads. This way, it also guarantees that the API will handle peak traffic well while keeping performance intact, and helps in bottleneck identification for performance.
5. Penetration Testing
It is also known as penetration testing, which simulates actual assaults on the API to find security holes that an attacker could exploit. Above and beyond that which is performed for routine security testing, this attempts to foil the security measures of the API. Organizations can prioritize remediating issues that would counteract potential attacks and assess their security posture through the use of penetration testing.
6. Fuzz Testing
Sending random or invalid inputs to the API is known as "fuzz testing," and it is used to find vulnerabilities or unexpected actions. It seeks to locate boundary conditions and edge instances that conventional scenarios could miss. It can also help to uncover problems such as crash, memory leak, or weird behaviors that endanger the stability of the program or could be exploited by an attacker.
7. Unit Testing
Validating individual API units or components apart from the system is the main goal of unit testing. It guarantees that every unit operates as intended and behaves appropriately. Developers write unit tests, which are then run as part of the build process to verify that certain methods, functions, or classes in the API codebase work as intended.
8. Performance Testing
Performance testing concerns the assessment of an API's responsiveness, throughput, and resource utilization while placing it under different loads and stress scenarios. This means ensuring that the API meets performance goals for expected workload situations while helping identify performance bottlenecks, such as slow database queries or inefficient code. It consists of:
- Load Testing: Assessing performance under expected load levels.
- Stress Testing: Software testing beyond normal load limits to determine breaking points.
- Endurance Testing: Evaluating performance over extended periods to assess stability and resource leaks.
Challenges of Automation API Testing
1. Proper Call Sequencing
When it comes to automation testing services, ensuring proper API functionality often entails executing a precise sequence of calls. Not doing so would lead to high rates of failure on the test than one would expect, especially when multi-threaded applications are invoked because they add considerable complications in the ordering of API calls. Such challenges make it imperative to do thorough planning and execution in API automation testing to maintain the reliability and accuracy of the entire testing process.
2. Handling Asynchronous Processing
Asynchronous operations and events, such message queues and real-time data streams, are frequently used in modern APIs. It can be challenging to test these asynchronous actions since you must wait for and confirm the completion of processes that don't respond right away. The test framework becomes more difficult when dependable methods for managing and validating asynchronous interactions are implemented.
3. Flakiness of Automated Tests
Automated tests may be flaky, passing or failing sometimes without requiring any modifications to the source. Numerous things, like timing problems, network instability, or reliance on outside services, could be to blame for this. Robust test design and consistent test environments are necessary to address flaky tests, which ruin trust in the testing process and can be challenging to identify and correct.
4. Numerous Integrations and Combinations
Software products that only use one API are rare in the market. Also, each new software component may cause the tested API's performance to suffer. There are more potential integration combinations the more APIs the product uses. For a QA team with limited resources, the sheer number of such combinations can present an additional barrier.
5. Maintenance of Test Scripts
During the development lifetime, API functions and endpoints frequently change. One of the biggest challenges is keeping the test scripts updated with these modifications. It takes a lot of work to update test scripts on a regular basis to account for API changes, like added endpoints, adjusted parameters, or changed answer formats. Failing to do so may lead to out-of-date tests that are unable to reliably validate the API's current state.
6. Integration with CI/CD Pipelines
Automated testing requires the integration of API tests into CI/CD pipelines, which might be difficult at times. Common problems include handling the additional burden on CI/CD infrastructure, maintaining test dependencies, and ensuring that tests run effectively inside the pipeline. Maintaining a responsive development process also requires setting up the pipeline to deliver useful feedback and alerts based on test findings.
Conclusion
In the software development market, automating your API testing process is not just a strategic advantage, but also a need. Teams can greatly improve the effectiveness, dependability, and scalability of their quality assurance activities by embracing automation. A software testing company can help implement API testing automation, making it possible to provide feedback on code changes quickly, identify problems early, and validate functionality consistently across various contexts. By guaranteeing that APIs function as intended under a range of circumstances, it lowers human error, quickens time-to-market, and enhances overall program quality. Integrating strong testing frameworks and techniques becomes essential as businesses progress toward continuous integration and deployment to provide resilient APIs that satisfy user expectations and endure real-world difficulties.


